Revestimiento de WPC Código HS para importación y exportación
Revestimiento de WPC Código HS para importación y exportación Cuando se trata de las industrias de la construcción y el diseño, la elección de los materiales desempeña un papel fundamental en la determinación de la estética, la durabilidad y la funcionalidad de las estructuras. Uno de estos materiales innovadores que ha acaparado una gran atención en los últimos años es el revestimiento de compuesto de madera y plástico (WPC). Este material compuesto,...
Revestimiento de WPC Código HS para importación y exportación
When it comes to the construction and design industries, the choice of materials plays a pivotal role in determining the aesthetics, durability, and functionality of structures. One such innovative material that has garnered significant attention in recent years is Wood Plastic Composite (WPC) cladding. This composite material, made from a blend of wood fibers and thermoplastics, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood products while providing a variety of benefits. As global trade continues to expand, understanding the import and export regulations surrounding WPC cladding, including the relevant Harmonized System (HS) codes, is essential for businesses operating in this sector.
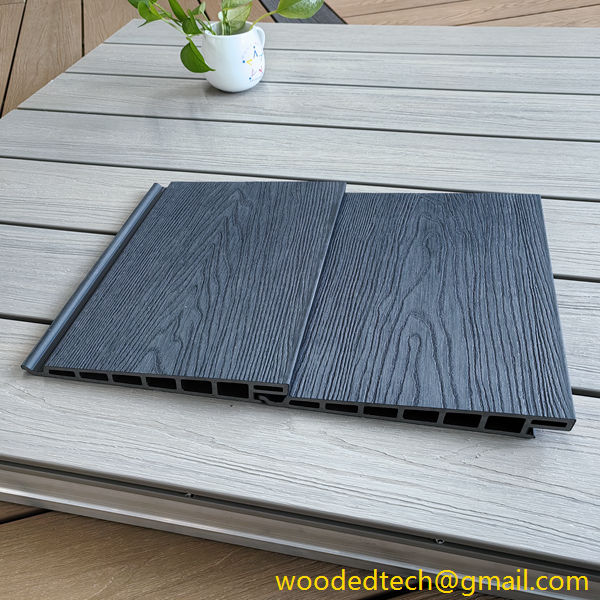
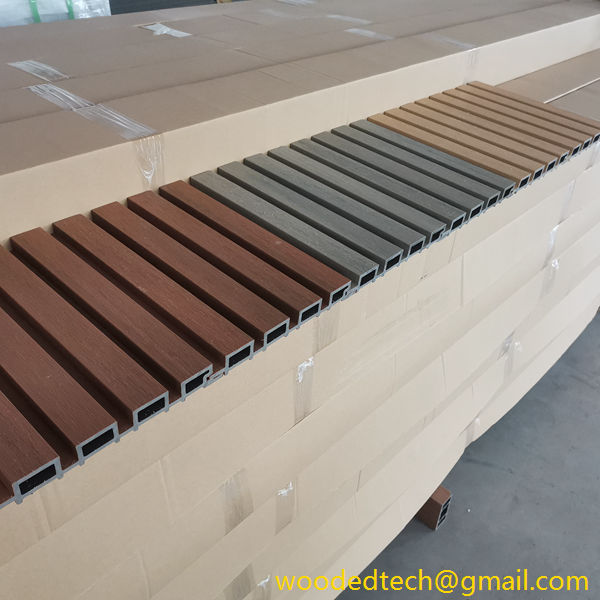
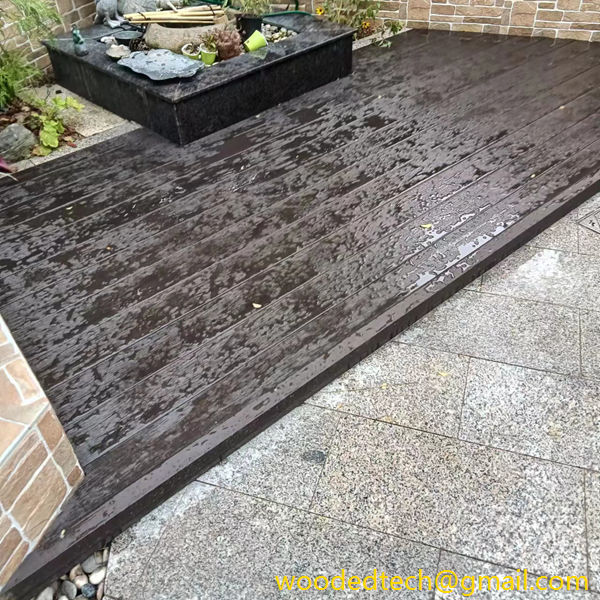
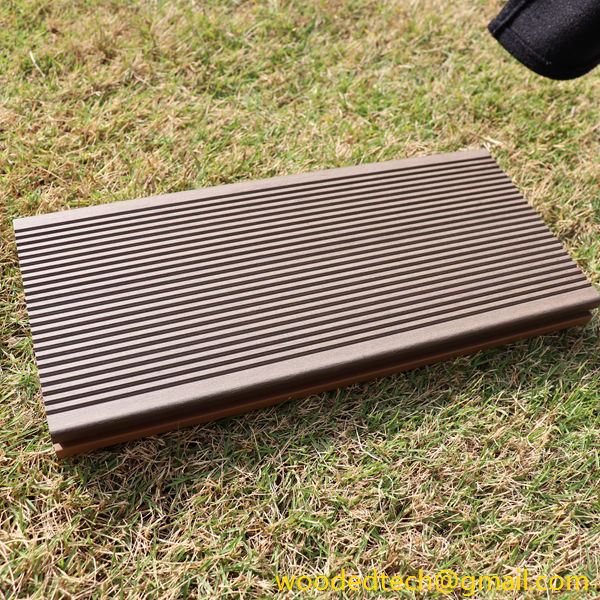
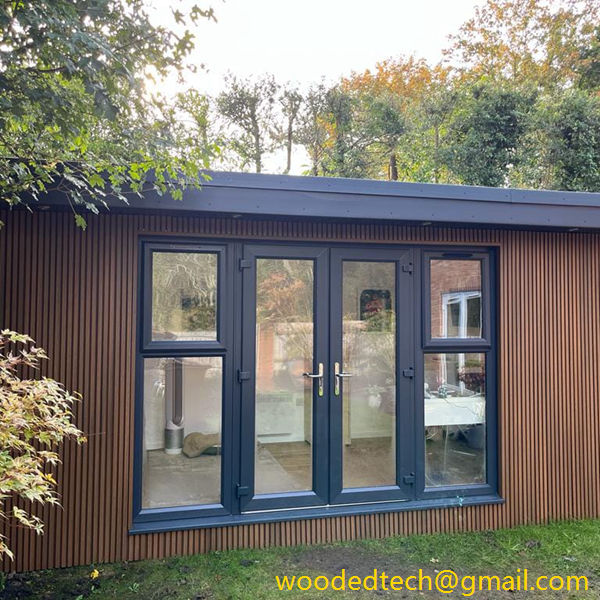
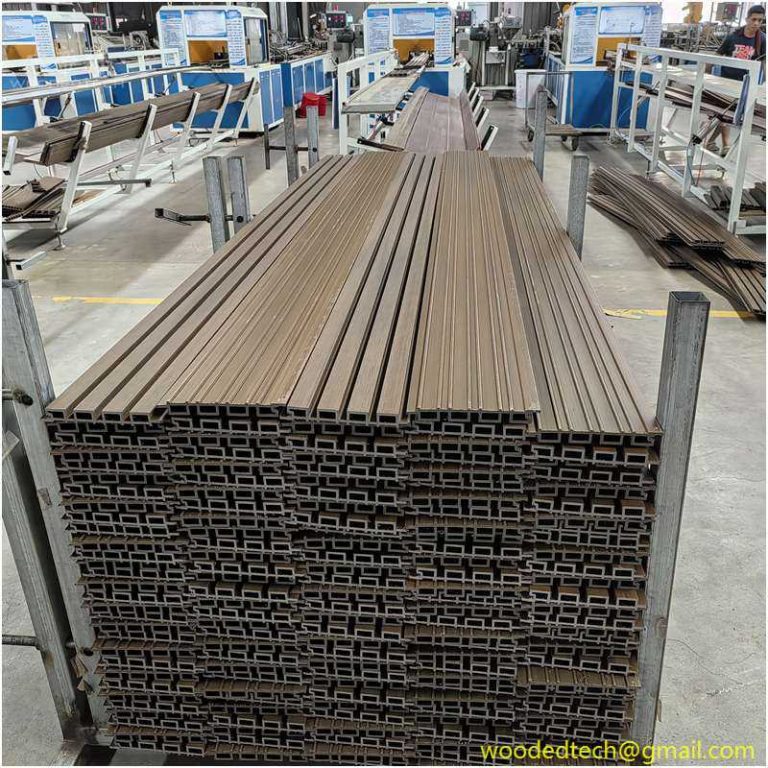
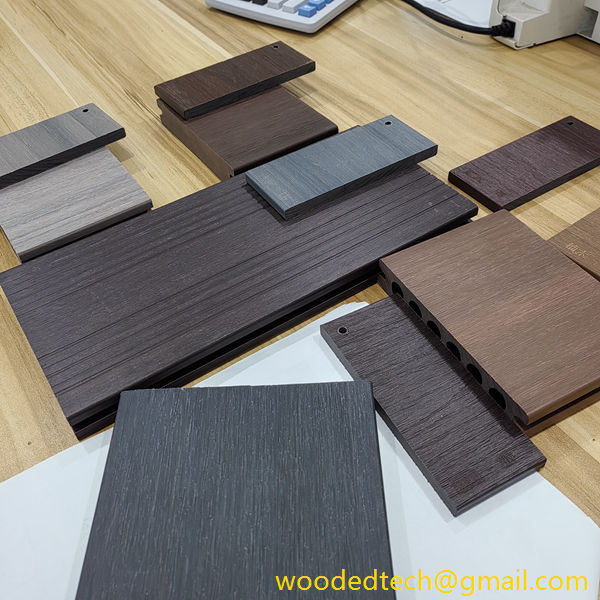
WPC cladding has become increasingly popular due to its versatility and customizable nature. It can be manufactured in various colors, textures, and finishes, allowing architects and designers to create unique looks that suit different architectural styles. One of the standout features of WPC cladding is its ability to mimic the appearance of natural wood while offering enhanced durability and resistance to the elements. This makes it an ideal choice for both residential and commercial applications, particularly in outdoor settings where exposure to moisture and UV rays can degrade traditional wood products.
The customizable nature of WPC cladding extends beyond its aesthetic appeal. Manufacturers can modify the composition of the material to enhance specific properties, such as improving fire resistance, increasing impact strength, or providing greater resistance to mold and mildew. This flexibility allows builders and designers to select WPC cladding that meets their specific requirements, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from high-rise buildings to private homes, and even landscaping projects.
As with any material that crosses international borders, WPC cladding is subject to import and export regulations. The Harmonized System (HS) code is a standardized numerical method of classifying traded products, which facilitates international trade by ensuring that products are uniformly categorized. For businesses involved in the trade of WPC cladding, understanding the correct HS code is crucial for compliance with customs regulations and for determining applicable duties and tariffs.
The HS code for WPC cladding typically falls within Chapter 39, which covers plastics and articles thereof. More specifically, WPC cladding is often classified under HS code 3918, which pertains to “Plates, sheets, film, foil, and strip, of plastics.” This classification can vary based on the specific composition of the material and its intended use, making it essential for traders to consult with customs experts or the relevant authorities to ensure accurate classification.
In addition to understanding the HS code, businesses must also be aware of other regulatory considerations when importing or exporting WPC cladding. This includes compliance with safety and environmental standards, as well as any labeling requirements that may be in place. Different countries may have varying regulations regarding the materials used in construction products, particularly concerning sustainability and toxicity. As WPC cladding is often marketed as an eco-friendly alternative, demonstrating compliance with these standards can enhance the material’s appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
Moreover, the global demand for sustainable building materials has been on the rise, driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues and a push for greener construction practices. WPC cladding, being made from recycled wood fibers and plastics, fits well within this trend. As a result, there has been a growing market for WPC products across various regions, including North America, Europe, and Asia. Businesses looking to enter these markets must not only navigate the complexities of import and export regulations but also stay informed about market trends and consumer preferences.
To enhance their competitiveness in the market, manufacturers of WPC cladding can also focus on innovation and product development. This may involve experimenting with new formulations that offer improved performance or exploring new applications for WPC materials. For instance, some companies are developing WPC products that incorporate additional features such as integrated lighting or smart technology, further expanding the possibilities for customization.
In conclusion, WPC cladding represents a significant advancement in the field of construction materials, offering a unique combination of sustainability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal. As businesses engage in the import and export of WPC cladding, understanding the relevant HS codes and regulatory requirements is essential for successful trade. Furthermore, by focusing on customization and innovation, manufacturers can position themselves favorably in a competitive marketplace that increasingly values sustainable building solutions. As the demand for eco-friendly materials continues to grow, WPC cladding stands out as a viable option for clients seeking both functionality and design excellence.