Madera de plástico falsa: La versatilidad de la madera de plástico falsa en diversas aplicaciones
Madera de plástico falsa: La versatilidad de la madera de plástico falsa en diversas aplicaciones En los últimos años, las industrias de la construcción y el diseño han recurrido cada vez más a materiales innovadores para satisfacer las demandas de evolución de la estética, la sostenibilidad y la funcionalidad. Un avance notable en este ámbito es el desarrollo de la madera de plástico falsa, también conocida como compuesto de madera y plástico (WPC)....
Madera de plástico falsa: La versatilidad de la madera de plástico falsa en diversas aplicaciones
In recent years, the construction and design industries have increasingly turned to innovative materials to meet the demands of evolving aesthetics, sustainability, and functionality. One notable advancement in this realm is the development of fake plastic wood, also known as wood-plastic composite (WPC). This versatile material has emerged as a popular alternative to traditional wood, appealing to a broad spectrum of applications ranging from decking and furniture to fencing and architectural elements. The distribution of global production capacity for fake plastic wood sheds light on its growing significance in various markets and its implications for sustainability and design.
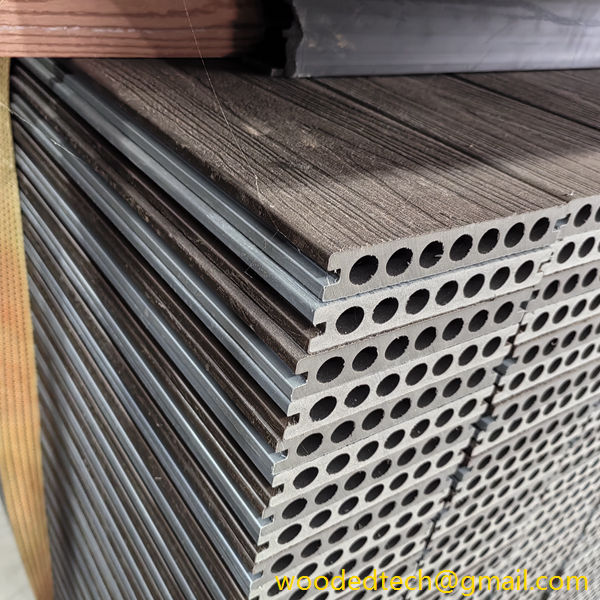
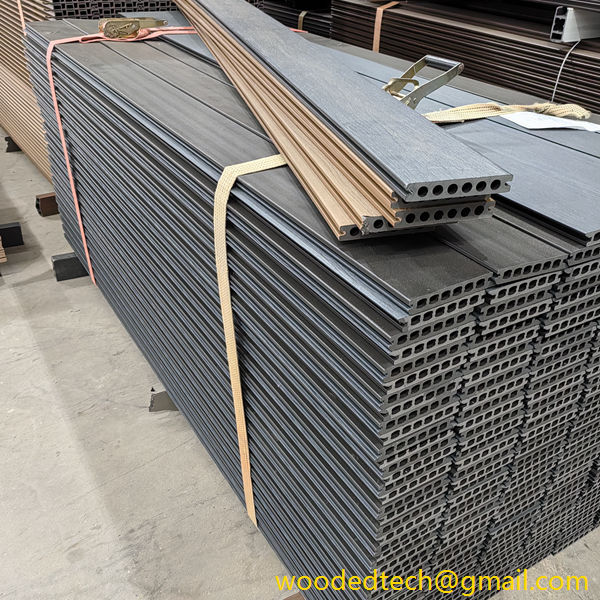
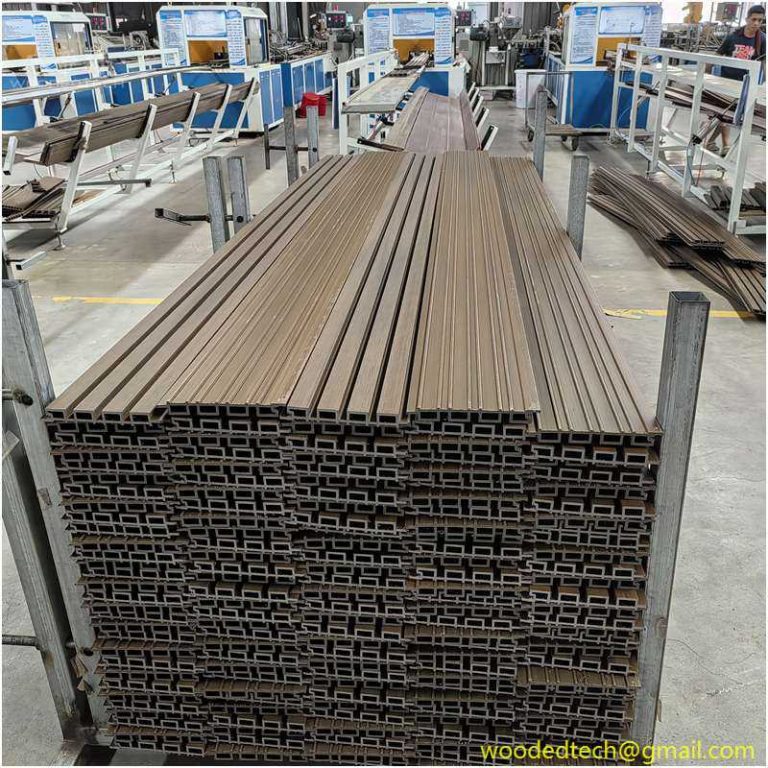
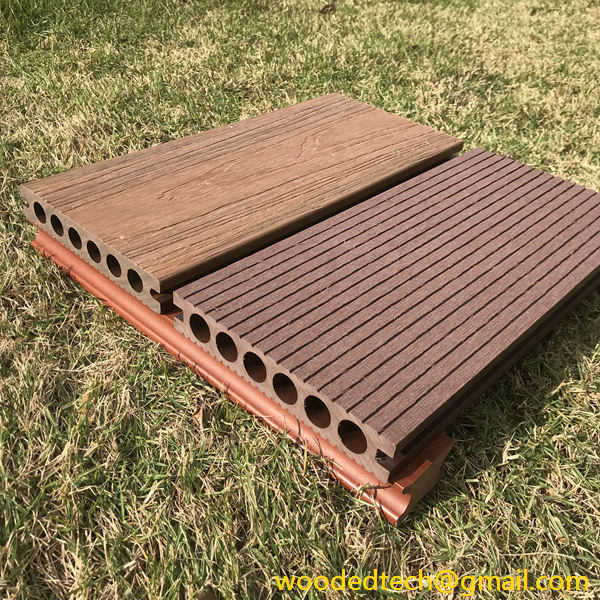
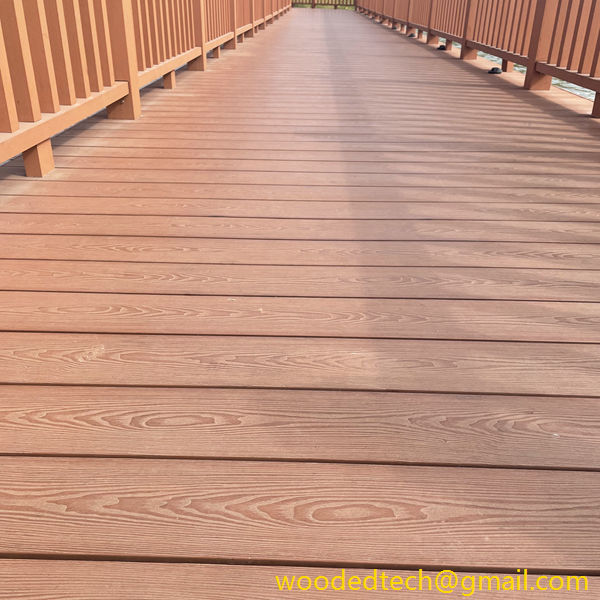
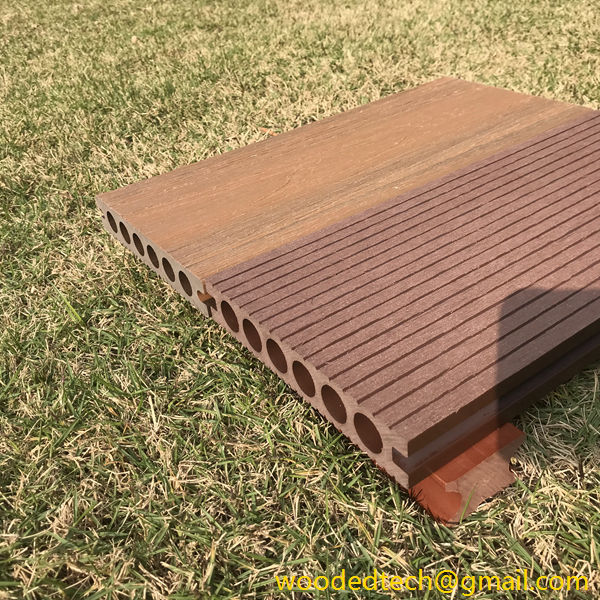
Fake plastic wood is primarily composed of a blend of wood fibers and thermoplastics, typically polyethylene or polypropylene. This combination allows for the creation of a material that mimics the appearance and texture of natural wood while offering enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors. As consumers and industries alike become more conscious of sustainability and environmental impact, fake plastic wood provides a solution that reduces deforestation and waste associated with traditional wood products.
One of the primary applications of fake plastic wood is in outdoor decking. Traditionally, wooden decks require significant maintenance, including regular staining and sealing, to preserve their appearance and longevity. In contrast, fake plastic wood is designed to withstand the elements without warping, splintering, or fading. This longevity not only reduces maintenance costs but also extends the life of the product, making it a cost-effective choice for homeowners and businesses. Additionally, the aesthetic versatility of fake plastic wood allows for a variety of finishes and colors, enabling designers to create outdoor spaces that align with contemporary trends while maintaining the warmth associated with natural wood.
Moreover, fake plastic wood is increasingly being used in furniture design. The furniture industry has seen a shift towards sustainable materials, and manufacturers are responding by incorporating wood-plastic composites into their products. This move is particularly evident in outdoor furniture, where durability and weather resistance are essential. Fake plastic wood can be molded into various shapes and styles, allowing designers to create innovative pieces that meet consumer demand for both form and function. The ease of maintenance compared to traditional wooden furniture further enhances its appeal, as consumers seek products that fit into their busy lifestyles without sacrificing aesthetic quality.
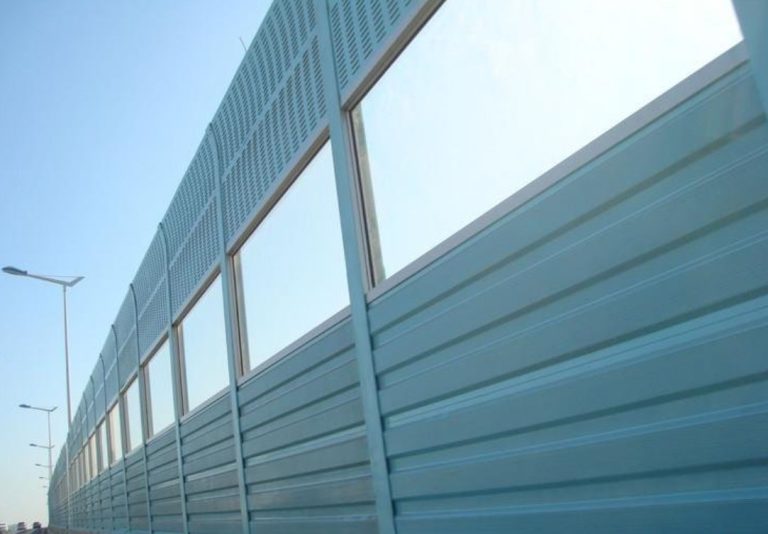
In addition to decking and furniture, fake plastic wood has found its way into fencing applications. Traditional wooden fences can suffer from rot, insect damage, and weather-related wear and tear, necessitating frequent repairs or replacements. Fake plastic wood fencing offers a durable, low-maintenance alternative that maintains its appearance over time. This has made it particularly popular in residential and commercial properties where aesthetic appeal and longevity are priorities. The adaptability of this material allows for various fencing styles, from classic picket fences to modern privacy screens, further broadening its market appeal.
The global production capacity distribution of fake plastic wood is noteworthy, as it reflects both regional manufacturing capabilities and market demand. North America has been a significant player in the production of wood-plastic composites, driven by strong consumer demand for sustainable building materials. The region’s advanced manufacturing technologies and emphasis on innovation have led to the development of a wide range of products, catering to both residential and commercial markets.
In Europe, the push for sustainability and environmental regulations has fueled growth in the production of fake plastic wood. The European Union has implemented policies aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting recycled materials, positioning WPC as an attractive alternative to traditional wood products. Countries like Germany, Sweden, and the Netherlands have seen increasing investments in WPC manufacturing, further enhancing their capacity to meet local and regional demands.
Asia-Pacific is also emerging as a significant player in the global production of fake plastic wood. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are witnessing a surge in demand for sustainable building materials driven by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. The region’s growing middle class is increasingly seeking eco-friendly products, prompting manufacturers to expand their production capabilities to meet this demand. Additionally, advancements in technology and manufacturing processes have enabled Asian producers to create high-quality wood-plastic composites at competitive prices.
The versatility of fake plastic wood extends beyond aesthetic applications; it also has potential in industries such as automotive, marine, and construction. In the automotive sector, for instance, WPC can be utilized in interior components, offering lightweight yet durable solutions that contribute to fuel efficiency. The marine industry benefits from the water-resistant properties of fake plastic wood, making it an ideal choice for boat decking and other applications exposed to harsh marine environments. In construction, WPC can be used in various structural elements, further emphasizing its adaptability across different sectors.
As the demand for sustainable and versatile materials continues to rise, fake plastic wood stands at the forefront of this movement. Its ability to mimic the beauty of natural wood while offering enhanced durability and reduced environmental impact makes it a valuable choice across multiple applications. The ongoing evolution of global production capacity for fake plastic wood reflects the growing recognition of its benefits, positioning it as a key player in the future of sustainable design and construction. As industries seek innovative solutions to address environmental challenges, the role of fake plastic wood is likely to expand, paving the way for a more sustainable future in material production and consumption.