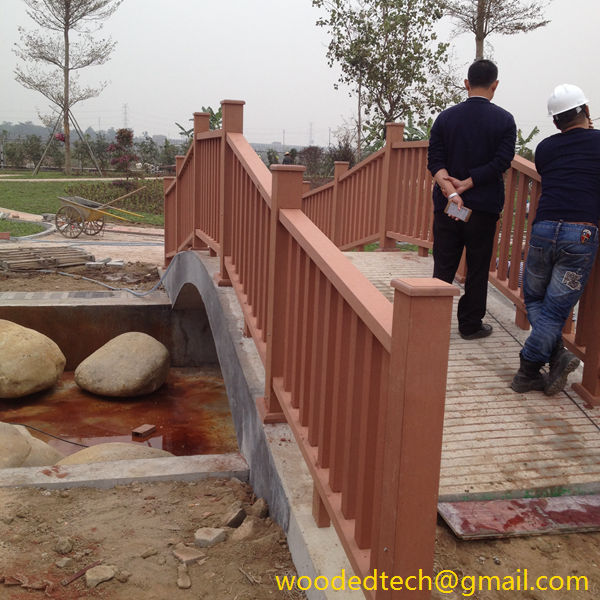
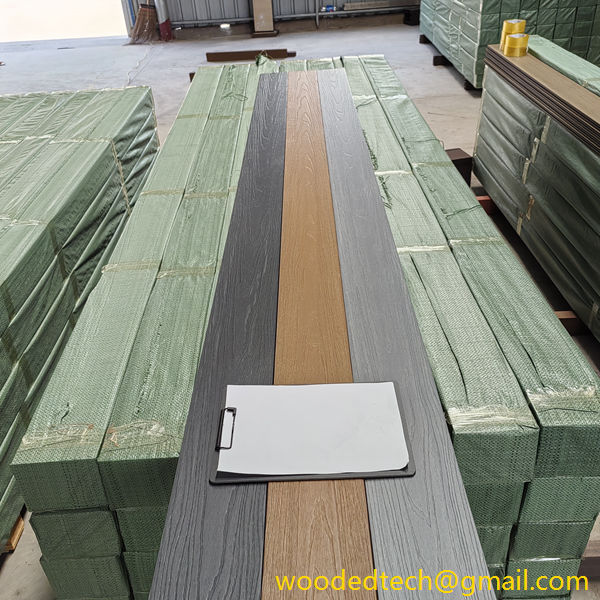
What type of decking clip should we choose when installing WPC decking?
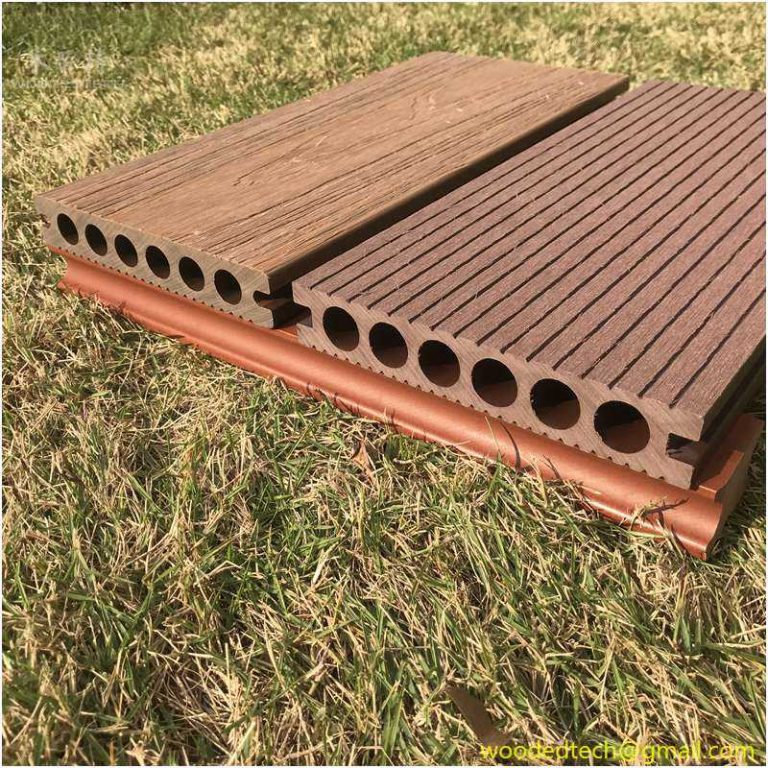
What type of decking clip should we choose when installing WPC decking? During the manufacturing process of WPC fasteners, due to different processes, they are mainly divided into two types: plastic injection molded fasteners and stainless steel stamped fasteners. Further classified by material, it can be further divided into different types such as PP, ABS,…
What type of decking clip should we choose when installing WPC decking?
During the manufacturing process of WPC fasteners, due to different processes, they are mainly divided into two types: plastic injection molded fasteners and stainless steel stamped fasteners. Further classified by material, it can be further divided into different types such as PP, ABS, 201 stainless steel, and 304 stainless steel. These different materials and processes result in significant differences in the value of fasteners.
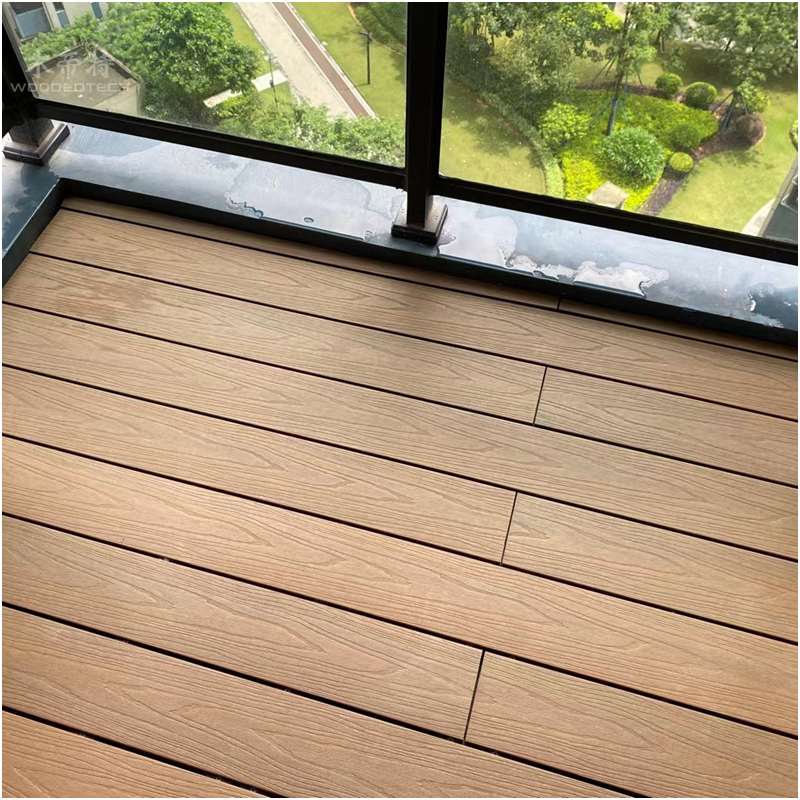
Most end users have insufficient understanding of the materials and installation methods of WPC decking, believing that floor fasteners are not important, as long as they can be installed and the price is cheap. However, in fact, this is not the case. According to relevant national standards, the water absorption size change rate of wood plastic flooring in the width direction must be less than or equal to 0.4%. This means that under normal circumstances, the floor width will have approximately 1mm expansion and contraction.
To meet this expansion and contraction requirement, it is necessary to reserve this gap on the fastener during installation. Therefore, selecting the appropriate fasteners has become crucial.
Only dovetail injection molded fasteners or square stainless steel fasteners can meet this requirement. If other types of fasteners are chosen, the 1mm elastic space for expansion and contraction of the board surface will be lost. Once the WPC decking expands due to water absorption or thermal expansion, due to the lack of reserved elastic space, the floor will compress each other, ultimately leading to arch deformation.